Deploying flask app on aws cloud
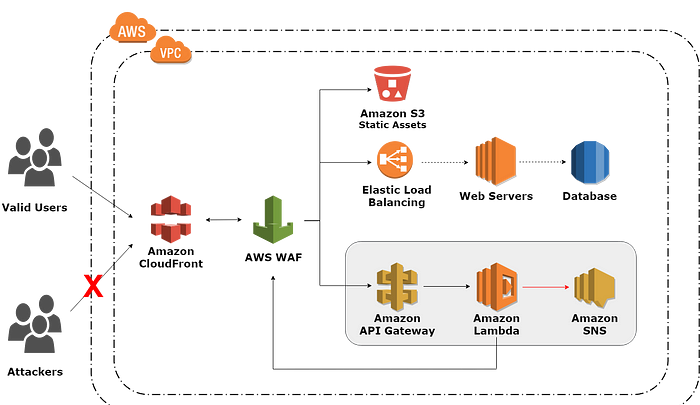
Summary: In this project, a library management system web application is deployed on Amazon Web Services cloud platform. In which -
- EC2 instances are auto-scaled with Elastic load balancer ELB to handle web traffic.
- The applciation is running on my domain www.**.me which is a hosted zone on Route53.
- Networking resources in AWS essential for hosting app on virtual private cloud VPC were created with cloudformation yaml script and automated with bash scripts.
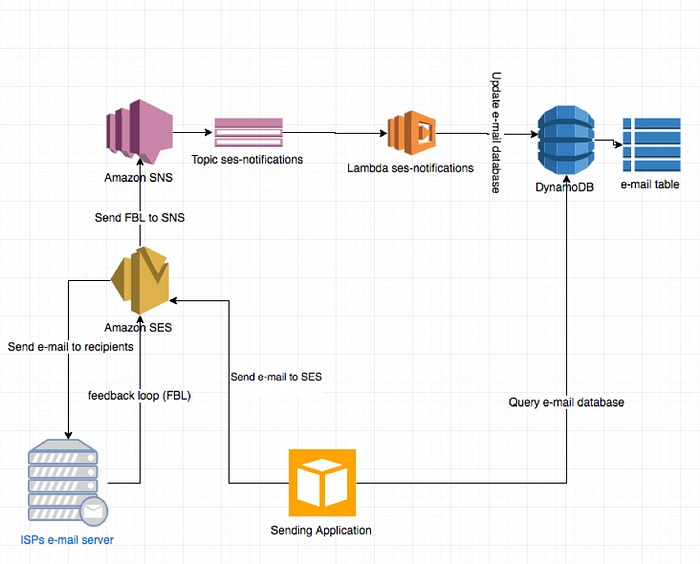
- The user is sent a password reset email via Simple Email Service SES by subscribing to Simple Notification Service SNS.
- The user’s email record is stored in DynamoDB table with a 15 minutes time-to-live TTL.
- The functionality operates on serverless computing with Lambda funtion.
- Images for books are stored in S3 bucket.
- Code deploy bundle is stored in different S3 bucket.
Check out the complete project here:
Technology stack
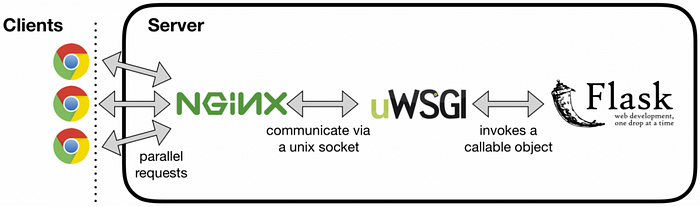
- Developed using Flask — a micro web framework written in Python.
- Plugged with uWSGI application server to launch the application.
- Nginx to act as a front end reverse proxy.
- Uses MySql for the relational database.
- Served on CentOS7.
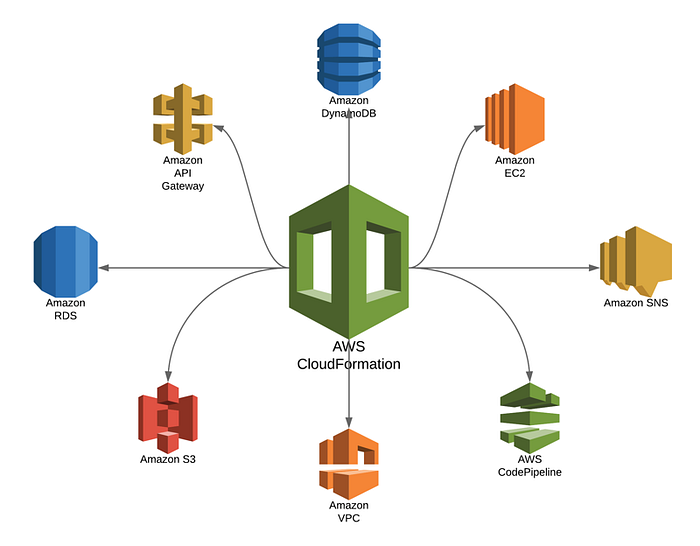
Cloudformation
Automating creation of all aws resources
- security groups — web, instance, rds
- internet gateway, VPC, subnets, route table
- dynamodb, rds, instance
- roles, policies
- user data to send to instance scripts can be found here
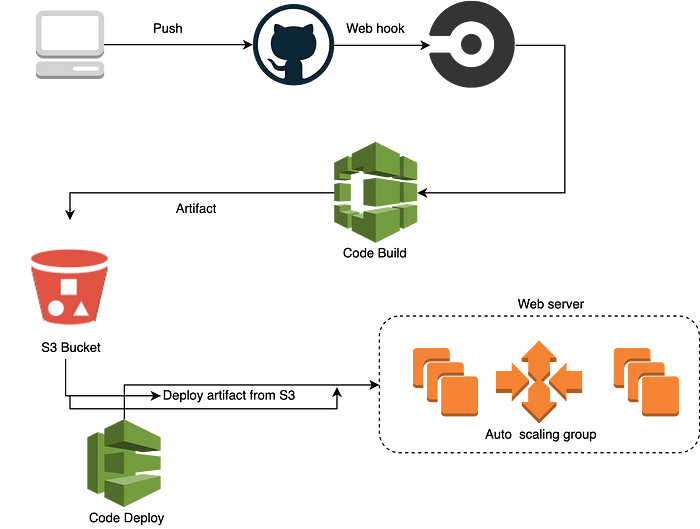
CI/CD
- CircleCI and AWS code-deploy are integraeted together in config.yaml script to test, zip and upload the all web applciation files onto code-deploy S3 bucket.
- While auto-scaling with load balancer, initially code will be deployed on 3 instances.
- Any changes made to master branch will trigger a new build
- refer appsepec.yml file in the root of the repository
Build instructions
Requirements:
- API testing tool — install Reslet plugin, which is a chrome’s extension
- User need to have two S3 buckets, eg:
- for webapp: yourdomain.tld
- for code deploy: code-deploy.yourdomain.tld
- where yourdomain.tld should be replaced with your domain name
git clone git@github.com:Adhira-Deogade/cloud-computing-aws.git cd cloud-computing-aws/webapp- Run a build through API without having to make any commit to master:
curl -u e7dc1223f96c97299b257a6cb26bffd9cf897bdc -d build_parameters[CIRCLE_JOB]=build https://circleci.com/api/v1.1/project/github/Adhira-Deogade/cloud-computing-aws/tree/master- refer config.yml file in .circleci folder
Identity Access Management(IAM) roles and policies
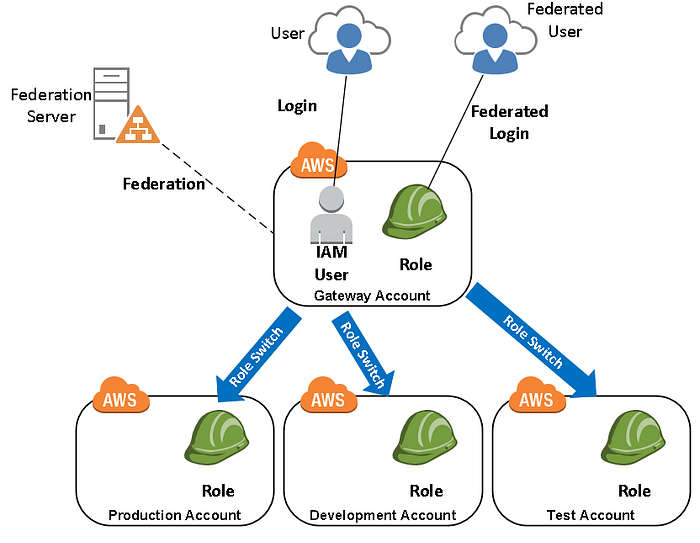
1. Group
Three groups:
- Administrator with admin access
- Staff with read only access
- Team with read only access
2. Users
- users in staff and team given accesss to sign-in into console with key and password (only read the resources)
- admin user with programmatic access — create and delete resources
- all users assigned to respective groups
3. Roles and policies
5 roles:
- Auto scaling service role has an attached policy of managing EC2 instances, cloud-watch agent, load balancer, instance profile, and simple notification service
- Elastic load balancer service role has an attached policy of managing network interface with instance, and logging.
- RDS service role has an attached policy of managing, logging, kinesis, and interfacing with instance.
- Support service role has an attached policy of supporting EC2, RDS, logging, cloudwatch, RDS, IAM, ELB, codebuild, codedeploy, cloudformation, api, s3, web-application-firewall.
- Trusted role with policy to manage trusted resources. Apart from AWS managed policies, I created following policies to manage aws resources:
Auto-scaling of EC2 instances
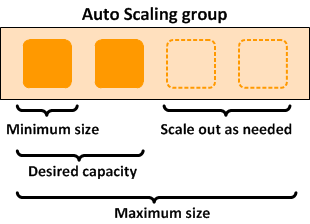
- Auto-scaling is important to make sure that the application is running irrespective of the load on the web-server.
- If there are around 1000 users simultaneously access the application, the server needs scaling and automatically new instances will be created, up and running to handle those API requests.
- I deployed the application on 3 EC2 instances and scaled max to 5 instances.
- Auto scaling group with attached security groups make it simple to manage the instances and code deployment.
Serverless computing — resetting password
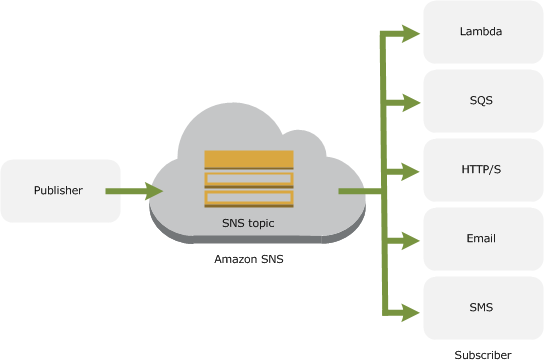
Lambda function
- This runs code in response to events and automatically manages the computing resources required by that code.
- This function is invoked when user requests to reset password through API.
- It subscribes to SNS topic
- Called “handler function”
Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- This event is triggered when API is hit
- Since lambda function is subscribed to this topic, it is executed when this event is triggered
Simple Email Service
- Email is composed with sender, receiver, subject and body
- Email is sent from the domain’s MX record
DynamoDB table
- Users email is stored in DynamoDB table
- TTL record field is defined during table creation
- python boto3 client will set it to 15 minutes in epoch time format
- after 15 minutes, the record loses its validity and sender needs to get another reset email
Integration:
Security
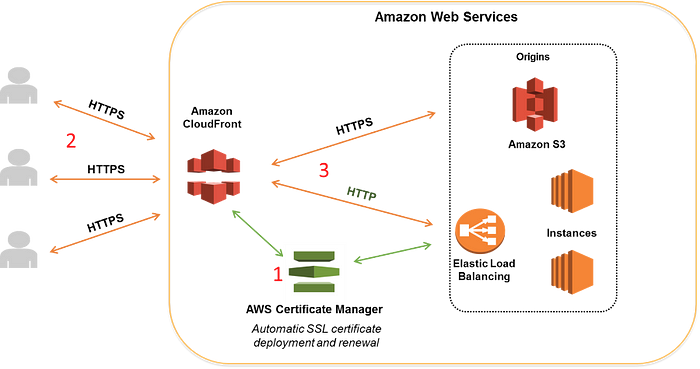
HTTPS
- Create an SSL certificate from here
- Validate with DNS by creating a CNAME record in Route 53
- To manage HTTPS traffic from load balancer to auto-scaling group instances, SSL certificate is essential
Security groups
- Web app security group — incoming and outgoing traffic to web application — open port 80
- Database security group — incoming and outgoing traffic to RDS instance — only web app can access the database and no one else outside the network. port 3306
- ELB security group — — incoming from 8080 and outgoing traffic 80 (web app)
Elastic load balancer
To handle multiple HTTP requests to web server, load balancer comes into effect

Python — SDK
boto3 client to create and implement aws resources
- s3 bucket — uploading images
- generating pre-signed URL — A user who does not have AWS credentials or permission to access an S3 object can be granted temporary access by using a pre-signed URL.
- email service (SES)
- notification service (SNS)
CloudWatch
- Cloudwatch agent (a JSON file) needs to be placed in the system on which the web server is running.
- It is setup in EC2 instances by installing them in the amazon machine image (AMI) — CentosOS7
wget https://s3.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/amazoncloudwatch-agent-us-east-1/centos/amd64/latest/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm sudo rpm -U ./amazon-cloudwatch-agent.rpm
- Cloudwatch logs
- To continuously monitor web application, use cloudwatch logs.
- Setting up logging config to lowest level of INFO, all important and trivial logs can be captured.
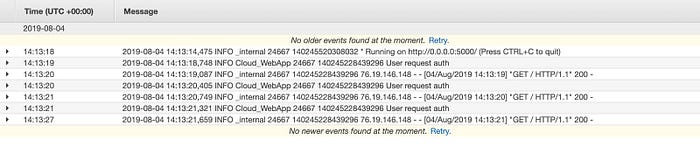
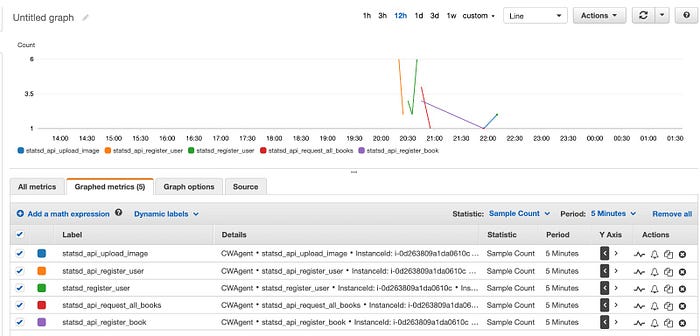
2. Cloudwatch metrics
- Metrics help to understand the value of each API end point. To obtain frequency, metrics can be used.
- In combination with statsd, flask-API end points can be monitored with AWS cloud watch.
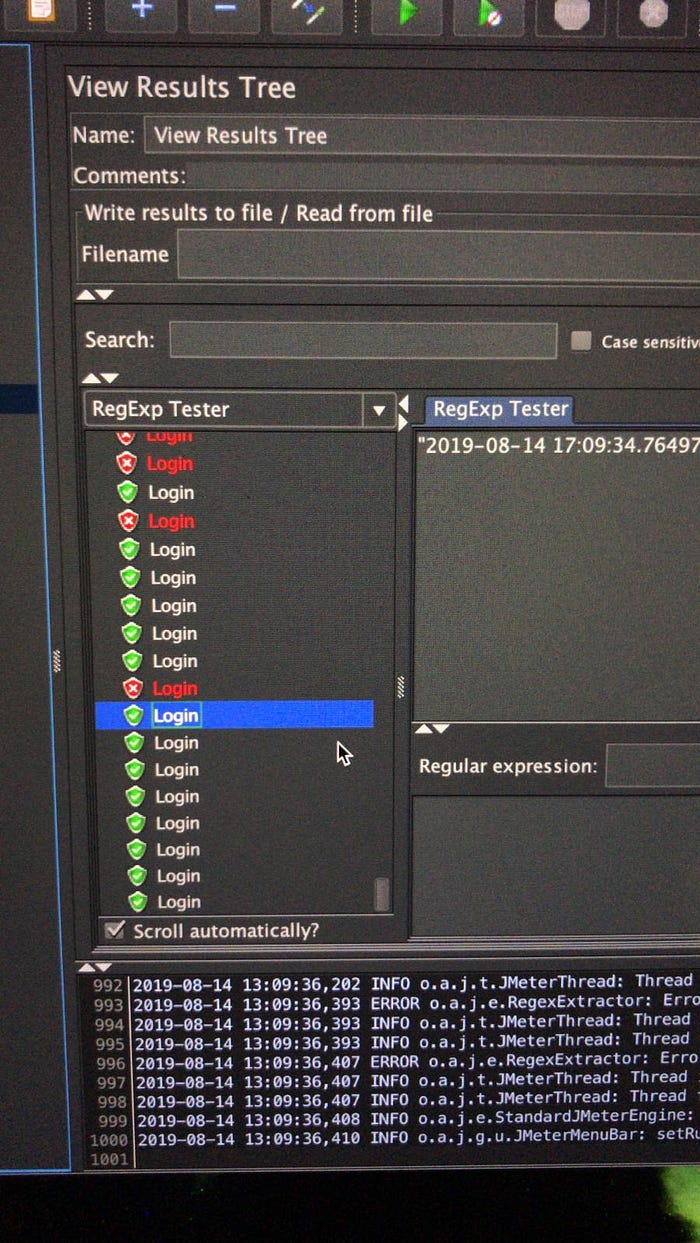
jmeter load testing
To test the auto-scaling of EC2 instances through load balancer, 1000 api requests are made continuously to increase load on web-server by calling following end-points -
- register user
- login
- register book
- get book details
- upload image to book
- Result: